Product Description
.
Special specifications products can be customized according to the customer request.
Hope you build up a long cooperation relationship with us; we will give you a discount and provide the free sample for your reference.
Looking CHINAMFG to your early inquiry.
| Products | Precision CNC machining parts | |
| Materials | Iron, aluminum, steel, copper, carbon steel, bronze, solder alloy, or as per the customers’ requirements. | |
| Dimensions | According to customer’ s drawing | |
| Surface treatment | Blacking, polishing, anodize, chrome plating, zinc plating, nickel plating, tinting or other as requirement. | |
| Packing | Bubble Bag, plastic bag, carton, plywood box, or as per the customer’ s requirements | |
| Standard | Such as ISO, DIN, GB, CHINAMFG and special standard | |
| Certificate | ISO9001: 2008 | |
| Processing equipment | CNC machine, CNC machining center, CNC cutting machine, radial drill, universal milling machine, high precision surface grinding machine, chamfering machine, etc. | |
| QC System | 100% during production check and random samples before shipment. | |
| Available | OEM, ODM | |
| MOQ | negotiable | |
| Ports | HangZhou or ZheJiang | |
| Delivery | Samples 7-15 days, batch production 30 days. |
CHINAMFG Transmission Technology is a professional manufacturer of lead screw, nuts, valve screw rod, worm and worm gear, which is used for transmission, lift, push-and-pull, fastening. We’re specialized in one-start lead screw, multi-start thread screw, left hand & right hand screw. Thread standard could be GB standard, German standard DIN103, American Standard ACME. The screw material could be carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, etc.; nuts material could be brass, tin-bronze, Al-bronze, POM, carbon steel, cast iron, free-cutting steel, etc. Special specifications products can be customized according to the your request, including lead screws, nuts, M0.5-M6 modulus of the worm and the worm gear.
We have a full array of suitable equipment which is more than 250 sets, such as CNC lathe, machine center, milling machine, grinding machine, two-axis rolling and three-axis rolling, punching. Products are now more widely used in many areas. such as smart home, elderly chair, smart lifting table, smart door opener, smart window opener, smart lift, valve, farming machinery, sports equipment and so on. Our products are popular in domestic and foreign market. We mainly export goods to Europe, America and other international markets, which are well received by customers. Welcome come to visit our factory for business discussion, we will do our best to provide you with quality products and service.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Type: | Round Head |
| Groove: | Trapezoidal |
| Connection: | Common Bolt |
| Head Style: | Round |
| Standard: | DIN, GB, ISO |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
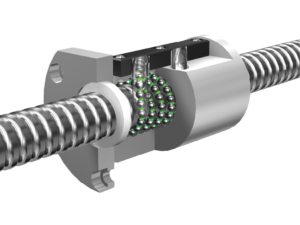
What role do lead screws play in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies?
Lead screws play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. They provide a reliable means of applying axial force to securely fasten components together. Here’s how lead screws contribute to alignment and tightness:
Alignment:
Lead screws aid in achieving proper alignment in mechanical assemblies through the following mechanisms:
- Linear Motion: Lead screws convert rotary motion into linear motion, allowing for controlled movement and alignment of components. By rotating the lead screw, the connected nut or threaded component moves along the screw’s axis, enabling precise positioning and alignment of the assembly.
- Thread Engagement: The mating threads of the lead screw and nut provide a positive mechanical connection. As the nut moves along the screw, the threads engage tightly, ensuring accurate alignment between the screw and the nut. This thread engagement helps maintain the desired position and alignment of components within the assembly.
- Guidance and Support: Lead screws often incorporate guidance mechanisms, such as linear bearings or sliding surfaces, to ensure smooth and accurate linear motion. These guidance systems help prevent lateral movement, minimize misalignment, and maintain the intended trajectory of the assembly, improving overall alignment.
- Positioning Accuracy: Lead screws offer precise positioning capabilities, allowing for the accurate alignment of components. The thread pitch and design, combined with the rotational input, enable controlled linear movement and positioning. This precision is critical in applications where proper alignment is essential for optimal performance and functionality.
Tightness:
Lead screws contribute to achieving tightness and secure fastening in mechanical assemblies through the following means:
- Axial Force Application: Lead screws transmit axial force to clamp or tighten components together. By rotating the lead screw, the axial force is applied through the nut or threaded component, generating a clamping action that holds the assembly tightly. This axial force helps prevent loosening, vibration, or unintended movement of the connected components.
- Self-Locking Capability: Lead screws possess a self-locking characteristic, which means they can hold their position without the need for additional locking mechanisms. The friction between the mating threads provides resistance to back-driving and helps maintain the tightness of the assembly. This self-locking property ensures that the assembly remains securely fastened, even in the absence of continuous power input.
- Thread Friction: The friction between the mating threads of the lead screw and nut contributes to the tightness of the assembly. When properly lubricated, the thread friction helps increase the resistance to loosening or undesired movement. By controlling the thread friction, the tightness of the assembly can be optimized to meet the specific requirements of the application.
- Preload Adjustment: Lead screws allow for preload adjustment, which is the intentional application of axial force to achieve a desired level of tightness. Preload can be applied by adjusting the initial position of the nut along the lead screw or by incorporating preload mechanisms, such as spring washers or Belleville washers. Preload optimization ensures that the assembly remains tight and secure, even under varying loads or external disturbances.
Overall, lead screws provide a reliable means of achieving proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. Their linear motion capabilities, thread engagement, guidance mechanisms, positioning accuracy, axial force application, self-locking capability, and preload adjustability all contribute to ensuring the stability, alignment, and tightness of the assembled components.
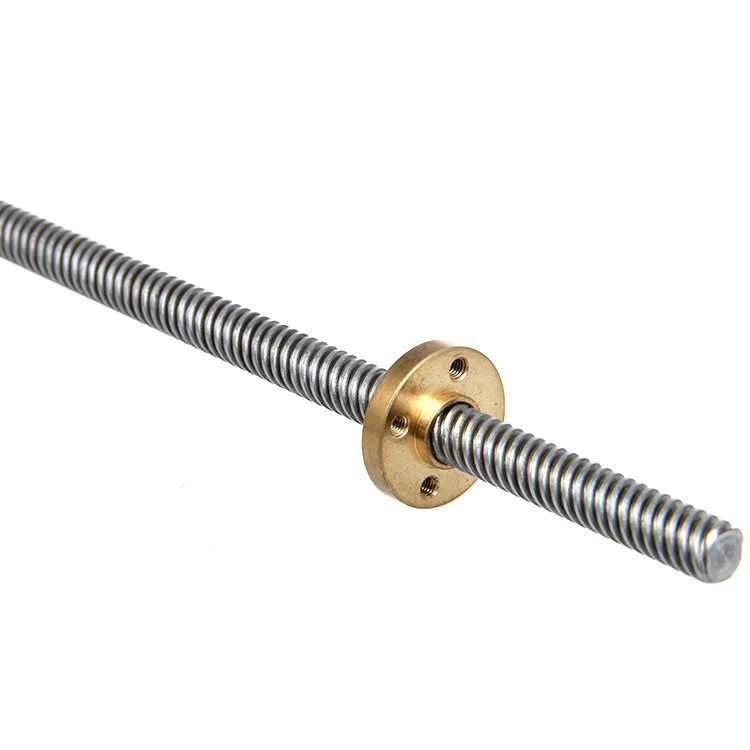

Can you provide insights into the importance of proper lead screw installation and alignment?
Proper lead screw installation and alignment are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of lead screw systems. The installation and alignment process directly affects the system’s accuracy, efficiency, and overall functionality. Here are some key insights into the importance of proper lead screw installation and alignment:
- Accuracy and Precision: Proper installation and alignment are essential for achieving accurate and precise linear motion. Misalignment or incorrect installation can introduce angular errors, axial misalignment, or parallelism issues, leading to positioning errors and reduced system accuracy. By following the manufacturer’s guidelines and using appropriate alignment tools, the lead screw can be installed in a way that minimizes misalignment and ensures precise movement and positioning.
- Load Distribution: Correct alignment during installation helps distribute the load evenly along the length of the lead screw. Proper alignment ensures that the load is shared uniformly between the screw and the nut, preventing excessive stress on specific areas. Improved load distribution reduces the risk of premature wear, deformation, or failure of the lead screw and enhances the overall durability and load-carrying capacity of the system.
- Backlash and Efficiency: Proper installation and alignment contribute to minimizing backlash in lead screw systems. Backlash, which refers to the clearance between the screw and nut, can negatively impact system performance, precision, and efficiency. Misalignment can exacerbate backlash issues, resulting in reduced repeatability and accuracy. By aligning the lead screw correctly, the backlash can be minimized, improving system efficiency and eliminating potential sources of error.
- Reduced Friction and Wear: Accurate installation and alignment help reduce friction and wear between the lead screw and nut. Misalignment can cause the screw and nut to rub against each other unevenly, leading to increased friction, accelerated wear, and reduced system lifespan. Proper alignment ensures that the mating surfaces are in optimal contact, minimizing friction and wear, and improving the overall efficiency and longevity of the lead screw system.
- System Stability and Vibration: Proper installation and alignment contribute to system stability and reduced vibration. Misalignment can introduce vibrations, resonances, or oscillations in the lead screw system, affecting the overall performance and potentially causing excessive noise or system instability. By aligning the lead screw correctly, the system’s natural frequencies can be maintained within acceptable limits, improving stability, reducing vibrations, and enhancing the system’s overall operation.
- Maintenance and Service: Proper installation and alignment simplify maintenance and service procedures. When lead screws are installed and aligned accurately, routine maintenance tasks such as lubrication, inspection, or component replacement can be performed more efficiently. Access to critical components is improved, and troubleshooting potential issues becomes easier, reducing downtime and enhancing the overall serviceability of the lead screw system.
In conclusion, proper lead screw installation and alignment are of utmost importance for achieving optimal performance, accuracy, efficiency, and durability of lead screw systems. Accurate alignment minimizes positioning errors, improves load distribution, reduces backlash and friction, enhances system stability, and simplifies maintenance procedures. By following manufacturer guidelines and utilizing appropriate alignment techniques, the benefits of proper installation and alignment can be realized, ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of lead screw systems.

Can you explain the role of a lead screw in converting rotary motion to linear motion?
A lead screw plays a crucial role in converting rotary motion into linear motion in mechanical systems. It achieves this by utilizing the helical threads on the screw and the corresponding threads on the nut. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a lead screw accomplishes the conversion:
- Helical Thread Design: A lead screw is designed with a helical thread that wraps around its cylindrical shaft. The thread is typically a continuous spiral groove with a specific pitch, which is the distance between adjacent threads. The pitch determines the linear distance the nut will travel when the lead screw makes one complete revolution.
- Matching Threaded Nut: The lead screw is paired with a nut that has threads matching those on the screw. The nut is typically fixed in place while the lead screw rotates. The nut contains internal threads that engage with the external threads of the lead screw.
- Rotary Motion: When the lead screw is rotated, either manually or by a motor-driven mechanism, the helical threads on the screw cause the nut to move linearly along the length of the screw. The direction and magnitude of the linear motion depend on the direction and speed of the screw’s rotation.
- Linear Motion: As the lead screw rotates, the engaged threads between the screw and the nut create a force that translates the rotational motion into linear motion. The helical threads on the screw push against the matching threads in the nut, causing the nut to move along the length of the screw. This results in linear displacement of the nut and any attached components.
- Precision and Control: The pitch of the lead screw determines the linear distance traveled by the nut for each revolution of the screw. By controlling the rotational motion of the lead screw, precise and controlled linear movement can be achieved. This makes lead screws suitable for applications that require accurate positioning or adjustment of components.
- Load Capacity: Lead screws can handle both axial loads (tension or compression forces) and torque. The helical threads distribute the load over a larger surface area, allowing the lead screw to support and transfer significant loads. By incorporating thrust bearings or other supporting elements, the lead screw can handle high loads while maintaining smooth and controlled linear motion.
Overall, the lead screw’s role in converting rotary motion to linear motion relies on the interaction between the helical threads of the lead screw and the matching threads of the nut. This mechanism provides a reliable and precise means to translate rotational motion into linear displacement, making lead screws a valuable component in various mechanical systems and applications.


editor by CX 2024-03-23
Leave a Reply