Product Description
Product Description
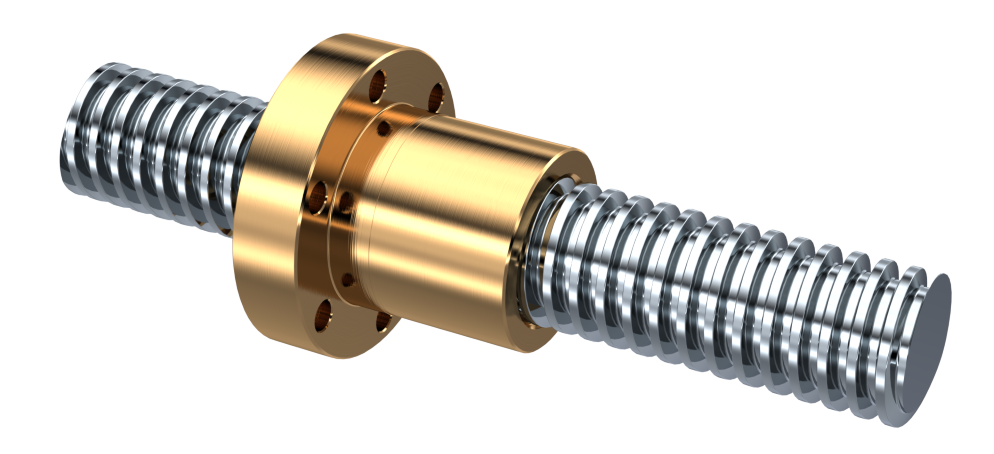
HIGH QUALITY ROLLED BALL SCREW :
Sketchs and dimensions
ROLLED BALL SCREW FSY SERIES SPECIFICATION
| Model no. | d | I | Da | Specification | Ca(kgf) | Coa(kgf) | kgf/ μm |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D | A | E | B | L | W | H | X | Q | n | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY01616-3.6 | 16 | 16 | 2.778 | 32 | 53 | 10.1 | 10 | 45 | 42 | 34 | 4.5 | M6 | 1.8×2 | 1073 | 2551 | 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY57120-3.6 | 20 | 20 | 3.175 | 39 | 62 | 13 | 10 | 52 | 50 | 41 | 5.5 | M6 | 1.8×2 | 1387 | 3515 | 37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY57125-3.6 | 25 | 25 | 3.969 | 47 | 74 | 15 | 12 | 64 | 60 | 49 | 6.6 | M6 | 1.8×2 | 2074 | 5494 | 45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY03232-3.6 | 32 | 32 | 4.762 | 58 | 92 | 17 | 12 | 78 | 74 | 60 | 9 | M6 | 1.8×2 | 3571 | 8690 | 58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY04040-3.6 | 40 | 40 | 6.35 | 73 | 114 | 19.5 | 15 | 99 | 93 | 75 | 11 | M6 | 1.8×2 | 4831 | 14062 | 70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY05050-3.6 | 50 | 50 | 7.938 | 90 | 135 | 21.5 | 20 | 117 | 112 | 92 | 14 | M6 | 1.8×2 | 7220 | 21974 | 86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model no. | d | I | Da | Specification | Ca(kgf) | Coa(kgf) | kgf/ μm |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D | A | E | B | L | W | H | X | Q | n | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY01632-1.6 | 16 | 32 | 2.778 | 32 | 53 | 10.1 | 10 | 42.5 | 42 | 34 | 4.5 | M6 | 0.8×2 | 493 | 1116 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY57140-1.6 | 20 | 40 | 3.175 | 39 | 62 | 13 | 10 | 48 | 50 | 41 | 5.5 | M6 | 0.8×2 | 653 | 1597 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY57150-1.6 | 25 | 50 | 3.969 | 47 | 74 | 15 | 12 | 58 | 60 | 49 | 6.6 | M6 | 0.8×2 | 976 | 2495 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY03264-1.6 | 32 | 64 | 4.762 | 58 | 92 | 17 | 12 | 71 | 74 | 60 | 9 | M6 | 0.8×2 | 1374 | 3571 | 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY04080-1.6 | 40 | 80 | 6.35 | 73 | 114 | 19.5 | 15 | 90 | 93 | 75 | 11 | M6 | 0.8×2 | 2273 | 6387 | 29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSY 0571 10-1.6 | 50 | 100 | 7.938 | 90 | 135 | 21.5 | 20 | 111 | 112 | 92 | 14 | M6 | 0.8×2 | 3398 | 9980 | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Detailed Photos
Part no. definition
Other series
FSU Series
| Model no. | Specification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| d | I | Da | D | A | B | L | W | H | X | Q | n | Ca(kgf) | Coa(kgf) | kgf/ μm |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU01605-4 ☆ | 16 | 5 | 3.175 | 28 | 48 | 10 | 45 | 38 | 40 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1380 | 3052 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU01610-3 | 10 | 3.175 | 28 | 48 | 10 | 57 | 38 | 40 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×3 | 1103 | 2401 | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57105-4 ☆ | 20 | 5 | 3.175 | 36 | 58 | 10 | 51 | 47 | 44 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 1551 | 3875 | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57105-4 ☆ | 25 | 5 | 3.175 | 40 | 62 | 10 | 51 | 51 | 48 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 1724 | 4904 | 45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57110-4 | 10 | 4.762 | 40 | 62 | 12 | 80 | 51 | 48 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 2954 | 7295 | 50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU03205-4 ☆ | 32 | 5 | 3.175 | 50 | 80 | 12 | 52 | 65 | 62 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 1922 | 6343 | 54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU03210-4 ☆ | 10 | 6.35 | 50 | 80 | 12 | 85 | 65 | 62 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 4805 | 12208 | 61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU04005-4 ☆ | 40 | 5 | 3.175 | 63 | 93 | 14 | 55 | 78 | 70 | 9 | M8 | 1×4 | 2110 | 7988 | 63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU5711-4 ☆ | 10 | 6.35 | 63 | 93 | 14 | 88 | 78 | 70 | 9 | M8 | 1×4 | 5399 | 15500 | 73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU 0571 1-4 ☆ | 50 | 10 | 6.35 | 75 | 110 | 16 | 88 | 93 | 85 | 11 | M8 | 1×4 | 6004 | 19614 | 85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU 0571 0-4 | 63 | 10 | 6.35 | 90 | 125 | 18 | 93 | 108 | 95 | 11 | M8 | 1×4 | 6719 | 25358 | 99 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU 0571 1-4 | 80 | 10 | 6.35 | 105 | 145 | 20 | 93 | 125 | 110 | 13.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 7346 | 31953 | 109 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU01204-4 | 12 | 4 | 2.5 | 24 | 40 | 10 | 40 | 32 | 30 | 4.5 | 1×4 | 902 | 1884 | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU01604-4 | 16 | 4 | 2.381 | 28 | 48 | 10 | 40 | 38 | 40 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 973 | 2406 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57104-4 | 20 | 4 | 2.381 | 36 | 58 | 10 | 42 | 47 | 44 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 1066 | 2987 | 38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57104-4 | 25 | 4 | 2.381 | 40 | 62 | 10 | 42 | 51 | 48 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 1180 | 3795 | 43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57106-4 | 6 | 3.969 | 40 | 62 | 10 | 54 | 51 | 48 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 2318 | 6057 | 47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU57108-4 | 8 | 4.762 | 40 | 62 | 10 | 63 | 51 | 48 | 6.6 | M6 | 1×4 | 2963 | 7313 | 49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU03204-4 | 32 | 4 | 2.381 | 50 | 80 | 12 | 44 | 65 | 62 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 1296 | 4838 | 51 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU03206-4 | 6 | 3.969 | 50 | 80 | 12 | 57 | 65 | 62 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 2632 | 7979 | 57 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU03208-4 | 8 | 4.762 | 50 | 80 | 12 | 65 | 65 | 62 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 3387 | 9622 | 60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU04006-4 | 40 | 6 | 3.969 | 63 | 93 | 14 | 60 | 78 | 70 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 2873 | 9913 | 66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU04008-4 | 8 | 4.762 | 63 | 93 | 14 | 67 | 78 | 70 | 9 | M6 | 1×4 | 3712 | 11947 | 70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU 0571 0-4 | 63 | 20 | 9.525 | 95 | 135 | 20 | 149 | 115 | 100 | 13.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 11444 | 36653 | 112 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU 0571 1-4 | 80 | 20 | 9.525 | 125 | 165 | 25 | 154 | 145 | 130 | 13.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 12911 | 47747 | 138 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSU1571-4 | 100 | 20 | 9.525 | 150 | 202 | 30 | 180 | 170 | 155 | 17.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 14303 | 60698 | 162 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
FSI Series
| Model no. | d | I | Da | Specification | Ca(kgf) | Coa(kgf) | kgf/ μm |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D | A | B | L | W | H | X | Y | Z | Q | n | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI01605-4 ☆ | 16 | 5 | 3.175 | 30 | 49 | 10 | 45 | 39 | 34 | 4.5 | 8 | 4.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1380 | 3052 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI01610-3 | 10 | 3.175 | 34 | 58 | 10 | 57 | 45 | 34 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×3 | 1103 | 2401 | 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI57105-4 ☆ | 20 | 5 | 3.175 | 34 | 57 | 11 | 51 | 45 | 40 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1551 | 3875 | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI57105-4 ☆ | 25 | 5 | 3.175 | 40 | 63 | 11 | 51 | 51 | 46 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 1724 | 4904 | 45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI57110-4 | 10 | 4.762 | 46 | 72 | 12 | 80 | 58 | 52 | 6.5 | 11 | 6.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 2954 | 7295 | 51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI03205-4 ☆ | 32 | 5 | 3.175 | 46 | 72 | 12 | 52 | 58 | 52 | 6.5 | 11 | 6.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 1922 | 6343 | 52 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI03210-4 ☆ | 10 | 6.35 | 54 | 88 | 15 | 85 | 70 | 62 | 9 | 14 | 8.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 4805 | 12208 | 62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI04005-4 ☆ | 40 | 5 | 3.175 | 56 | 90 | 15 | 55 | 72 | 64 | 9 | 14 | 8.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 2110 | 7988 | 59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI5711-4 ☆ | 10 | 6.35 | 62 | 104 | 18 | 88 | 82 | 70 | 11 | 17.5 | 11 | M8 | 1×4 | 5399 | 15500 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI 0571 1-4 ☆ | 50 | 10 | 6.35 | 72 | 114 | 18 | 88 | 92 | 82 | 11 | 17.5 | 11 | M8 | 1×4 | 6004 | 19614 | 83 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI 0571 0-4 | 63 | 10 | 6.35 | 85 | 131 | 22 | 93 | 107 | 95 | 14 | 20 | 13 | M8 | 1×4 | 6719 | 25358 | 95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI 0571 1-4 | 80 | 10 | 6.35 | 105 | 150 | 22 | 93 | 127 | 115 | 14 | 20 | 13 | M8 | 1×4 | 7346 | 31953 | 109 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI01604-4 | 16 | 4 | 2.381 | 30 | 49 | 10 | 45 | 39 | 34 | 4.5 | 8 | 4.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 973 | 2406 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI57104-4 | 20 | 4 | 2.381 | 34 | 57 | 11 | 46 | 45 | 40 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1066 | 2987 | 37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI5715T-4 | 5.08 | 3.175 | 34 | 57 | 11 | 51 | 45 | 40 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1550 | 3875 | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI57104-4 | 25 | 4 | 2.381 | 40 | 63 | 11 | 46 | 51 | 46 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1180 | 3795 | 43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI5715T-4 | 5.08 | 3.175 | 40 | 63 | 11 | 51 | 51 | 46 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 5.5 | M8 | 1×4 | 1724 | 4903 | 45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FSI03204-4 | 32 | 4 | 2.381 | 46 | 72 | 12 | 47 | 58 | 52 | 6.5 | 11 | 6.5 | M6 | 1×4 | 1296 | 4838 | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Company Profile
ZheJiang CHINAMFG Precision Technology Co.,Ltd.
is a professional manufacturer of linear guide, linear module and ball screw etc.she is located in HangZhou city,ZheJiang ,China.The production base covers 33333 square CHINAMFG and holds a building area of 16000 square CHINAMFG at present. with over 10 years’ effort of our whole team. and also trust and support from our respected customers. We are so lucky to become 1 famous brand in China, who make international standard products.we aim to serve customers world-widely.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 1-10mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 4-Row |
| Nut Type: | Circulator |
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Can you provide examples of products or machinery that use lead screws for precise positioning?
Lead screws are widely utilized in various products and machinery that require precise positioning. Here are some examples of products and machinery that commonly use lead screws for precise positioning:
- CNC Machines: Computer numerical control (CNC) machines, including CNC mills, lathes, and routers, use lead screws to precisely position the cutting tools or workpieces. Lead screws enable accurate and repeatable movement in the linear motion systems of these machines, allowing for precise machining operations.
- 3D Printers: Lead screws are extensively used in 3D printers to control the movement of the print head or build platform. They enable precise positioning of the print head, ensuring accurate layer-by-layer deposition of the printing material, resulting in high-quality 3D prints.
- Robotics: Lead screws are integral to robotic systems that require precise positioning. They are used in robotic arms to control the movement and positioning of the end effectors or grippers. Lead screws provide accurate and controlled linear motion in robot joints, allowing for precise and coordinated movements in industrial, medical, and research robotics.
- Medical Imaging Systems: Lead screws are employed in medical imaging systems, such as computed tomography (CT) scanners and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, to precisely position the patient bed or gantry. This precise positioning is crucial for accurate imaging and diagnosis.
- Laboratory Automation Equipment: Lead screws are used in laboratory automation equipment, such as liquid handling robots and sample handling systems, for precise positioning and movement of samples, reagents, and labware. They ensure accurate and repeatable positioning required for various laboratory processes.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment: Lead screws are utilized in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, including wafer handling systems and lithography machines. They provide precise positioning and movement of wafers, masks, and other components critical for semiconductor fabrication processes.
- Camera Sliders: Lead screws are employed in camera sliders used in photography and videography applications. They enable smooth and precise linear motion of the camera along the slider, allowing for controlled tracking shots and precise camera positioning.
- Telescopes and Astronomy Equipment: Lead screws are utilized in telescopes and other astronomy equipment to precisely position optical components and achieve accurate tracking of celestial objects. They enable fine adjustments and precise pointing of telescopes for astronomical observations.
- Industrial Inspection Systems: Lead screws are used in industrial inspection systems, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical inspection systems, for precise movement and positioning of the inspection probes or cameras. This ensures accurate measurement and inspection of manufactured components.
These are just a few examples of the products and machinery that utilize lead screws for precise positioning. The versatility, accuracy, and reliability of lead screws make them a preferred choice in applications that require controlled linear motion and precise positioning of components.

How do electronic or computer-controlled components integrate with lead screws in modern applications?
In modern applications, electronic or computer-controlled components play a crucial role in integrating with lead screws to enhance functionality, precision, and automation. These components enable advanced control, monitoring, and feedback capabilities, allowing for more efficient and accurate operation of systems incorporating lead screws. Here are some ways electronic or computer-controlled components integrate with lead screws in modern applications:
- Position Control: Electronic control systems can precisely control the position of the lead screw by monitoring and adjusting the rotational movement of the motor driving the screw. Position feedback sensors, such as encoders or linear scales, provide real-time information about the screw’s position, allowing the control system to accurately position the load. This integration enables precise positioning and highly repeatable motion control in applications such as CNC machinery, 3D printers, or robotic systems.
- Speed and Velocity Control: Electronic control systems can regulate the speed and velocity of the lead screw by controlling the motor’s rotational speed. By adjusting the motor speed, the control system can achieve specific linear speeds or velocity profiles along the length of the lead screw. This integration is particularly useful in applications where controlled acceleration, deceleration, or dynamic speed changes are required, such as automated manufacturing processes or motion control systems.
- Force and Torque Control: In some applications, it is necessary to control the force or torque applied by the lead screw. Electronic control systems can monitor and adjust the motor’s current or voltage to regulate the applied force or torque. This integration allows for precise force control, load balancing, or torque limiting in applications such as material testing machines, automated assembly systems, or lifting mechanisms.
- Automation and Synchronization: Electronic or computer-controlled components facilitate the automation and synchronization of multiple lead screws or other mechanical components. Through centralized control, these components can coordinate the movements of multiple lead screws, ensuring precise and synchronized motion. This integration is commonly used in complex systems with multiple axes of motion, such as multi-axis CNC machines or robotic systems.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics: Electronic control systems can monitor the operating parameters of lead screws, such as temperature, vibration, or load conditions. By integrating sensors and monitoring algorithms, the control system can detect abnormal conditions, provide real-time feedback, and trigger appropriate actions, such as alerting maintenance personnel or implementing protective measures. This integration enhances system reliability, prevents failures, and enables predictive maintenance in applications where lead screw performance is critical.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Electronic or computer-controlled components often provide a user interface through which operators can interact with the lead screw system. HMIs allow operators to input commands, monitor system status, and receive feedback. This integration simplifies system operation, enables parameter adjustments, and facilitates troubleshooting or diagnostics.
In summary, electronic or computer-controlled components play a vital role in integrating with lead screws in modern applications. Position control, speed and velocity control, force and torque control, automation and synchronization, monitoring and diagnostics, and human-machine interface capabilities enhance the functionality, precision, and automation of systems incorporating lead screws. This integration enables advanced control, improved performance, and enhanced operational capabilities in various industries and applications.

Are there specific advantages to using lead screws over other linear motion systems?
Yes, there are specific advantages to using lead screws over other linear motion systems. Here are some of the advantages associated with lead screws:
- Precision and Accuracy: Lead screws offer precise and accurate linear motion control. The thread design and pitch allow for precise positioning and movement of components, making them suitable for applications that require high levels of accuracy and repeatability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lead screws are often more cost-effective compared to other linear motion systems, such as ball screws or linear actuators. They provide a reliable and efficient solution for converting rotary motion into linear motion at a relatively lower cost, making them a popular choice for many applications.
- High Load Capacity: Lead screws are capable of handling significant axial loads and torque. The thread engagement between the screw and nut distributes the load over a larger surface area, allowing lead screws to support and transfer substantial loads. This makes them suitable for applications that require heavy-duty performance and load-carrying capabilities.
- Self-Locking: Lead screws have a self-locking characteristic, which means they can hold their position without the need for additional locking mechanisms. The friction between the mating threads helps prevent back-driving and maintains the position of the load, providing stability and safety in applications where holding the position is critical.
- Simple Design and Installation: Lead screws have a relatively simple design, consisting of a screw and a nut. This simplicity makes them easier to install and maintain compared to more complex linear motion systems. Additionally, the straightforward design allows for customization and modification to meet specific application requirements.
- Efficiency: Lead screws can achieve high mechanical efficiency in converting rotary motion to linear motion. The efficiency depends on factors such as the thread design, lubrication, and preload. With proper design and lubrication, lead screws can operate with minimal friction and energy loss, ensuring efficient power transmission.
- Versatility: Lead screws can be used in a wide range of applications across various industries. They are suitable for applications that require linear motion, precise positioning, or adjustment of components. Lead screws find applications in industries such as manufacturing, automation, robotics, aerospace, medical, and more.
These advantages make lead screws a popular choice in many applications where precise linear motion control, cost-effectiveness, high load capacity, and simplicity are essential. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and factors such as speed, accuracy, duty cycle, and environmental conditions when selecting the appropriate linear motion system.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
Leave a Reply